Copyright © 2022 Foshan MBRT Nanofiberlabs Technology Co., Ltd All rights reserved.Site Map
Specifically, electrospinning technology faces the following challenges in industrial mass production:
The composition, flow rate, voltage and other parameters of spinning solution have great influence on the morphology, size and structure of nanofibers. In industrial production, it is necessary to strictly control the preparation of spinning solution to ensure the stable quality of nanofibers.

The development of electrostatic spinning equipment needs to consider factors such as yield, cost and reliability. At present, the output of electrostatic spinning equipment is still unable to meet the needs of industrial production, and the cost of equipment is high.
The post-treatment process can improve the properties of nanofibers, such as strength and wear resistance. In industrial production, it is necessary to optimize the post-treatment process to improve the performance and stability of nanofibers.

To solve these difficulties, the MBRT Nanofiberlabs team can help you with the feasibility study of pilot production, as follows:
1. Understand the prototype product: Understand the prototype product of the laboratory, including its material composition, structure, performance and other information. Based on the experience in pilot, pilot and mass production facilities, the Easgang team analyzed the production process of the prototype product and evaluated its feasibility at pilot production scale.
2. Provide equipment support: According to your needs, provide pilot equipment support, so that you can conduct pilot production on actual equipment.
3. Provide technical support: in the process of pilot production, we will provide you with technical support and guidance to solve the problems and challenges encountered in the production process to ensure the smooth progress of pilot production.
Related product link:
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/products-category/production-line.html
Needle spinning and needle-free spinning are the two main methods of electrospinning. Needle spinning is the use of the electrostatic force generated by the tip of the needle to quickly evaporate the solvent in the spinning solution to form nanofibers.

1. High output: The output of needle spinning is higher, up to tens to hundreds of meters per hour.
2. Low equipment cost: The cost of needle spinning equipment is low, suitable for small and medium-sized production.
1. Fiber topography is not uniform: the fiber topography of needle spinning is not uniform, easy to appear fiber fracture, accumulation and other problems.
2. Low fiber strength: The strength of needle-spun fibers is low and not suitable for applications with high strength requirements.
Needle-free spinning is a technology that uses the electrostatic force generated by the nozzle to vaporize the solvent in the spinning solution quickly and form nanofibers.

1. Uniform fiber appearance: The fiber appearance of needle-free spinning is uniform, and the size, shape and structure of the fiber can be controlled.
2. High fiber strength: The fiber strength of needle-free spinning is high, which can meet the application of high strength requirements.
1. Low output: The output of needle-free spinning is low, up to several meters to tens of meters per hour.
2. High equipment cost: The cost of needle-free spinning equipment is high, suitable for large-scale production.
When selecting electrospinning large-scale production equipment, the following factors need to be considered:
Such as output requirements, fiber performance requirements, investment costs, etc., the specific choice of equipment, but also need to be considered according to your actual needs, you need to find a professional team to assist you to choose, after all, professional people do professional things. If you have these needs, you can find MBRT Nanofiberlabs team to help you provide technical support and equipment support, as well as high-end technical information for mass production.
Related product link:
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/products-category/production-line.html
Many people now use electrospinning technology for the following reasons:
1. The cost of preparing nanofibers is low: compared with other technologies, electrospinning technology has simple equipment, convenient operation and low cost;
2. The nanofibers prepared are of high quality: the electrospinning technology can prepare high-quality and evenly distributed nanofibers, and the fiber diameter can be adjusted in a wide range;
3. Wide range of application: electrospinning technology can be used to prepare nanofibers of various materials, including polymers, inorganic materials, etc., with a wide range of application;
4. Can achieve large-scale production: electrostatic spinning technology can achieve continuous production, suitable for industrial production needs.
MBRT Nanofiberlabs has developed a variety of laboratory electrospinning machine to prepare nanofibers.
E02S
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/professional-electrospinning-machine-e03.html

E04S
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/multifunctional-electrospinning-machine-e04-001.html

E05S
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/all-round-electrospinning-machine-e06.html

In recent years, great breakthroughs have been made in the macro preparation of electrospinning nanofibers, mainly including the following aspects:
Conventional electrospinning techniques typically use only a single nozzle, which limits the yield of nanofibers. Multi-nozzle electrospinning technology can use multiple nozzles at the same time, thereby greatly increasing the yield of nanofibers. At present, electrostatic spinning devices with dozens or even hundreds of nozzles have been developed, which can achieve continuous and large-scale production of nanofibers.

Rotary cylinder electrospinning technology is a new type of electrospinning technology, which uses a high-speed rotating cylinder to collect nanofibers. This technique can produce a uniform and continuous nanofiber film, and can realize the macro preparation of nanofibers.

Air assisted electrospinning technology uses air to assist the formation and collection of nanofibers. This technique can improve the yield and uniformity of nanofibers, and can prepare nanofibers with different morphologies and structures.

Electrospinning-melt-blown composite technology combines electrospinning technology with melt-blown technology to prepare nanofiber membranes with bilayer structure. This nanofiber membrane has excellent filtration properties and mechanical properties, making it ideal for use in fields such as air filtration and protective clothing.

In addition, there are many other technologies that are also being developed to improve the yield and quality of electrospun nanofibers. For example: plasma assisted electrospinning technology, ultrasonic assisted electrospinning technology, electric field induced electrospinning technology.
Related product link:
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/products-category/production-line.html
The techniques for preparing nanofibers mainly include the following:




E02S
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/professional-electrospinning-machine-e03.html

E04S
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/multifunctional-electrospinning-machine-e04-001.html

E05S
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/all-round-electrospinning-machine-e06.html

The composite of nanoparticles and nanoparticles can integrate different kinds or different properties of nanoparticles to achieve versatility. In the medical field, nanoparticle and nanoparticle composites are widely used in drug delivery systems, which can achieve accurate drug delivery, controlled release, improve treatment effectiveness and reduce side effects.
Through rational design and composite nanoparticles, the material properties can be diversified and optimized. Electrostatic spraying and ultrasonic spraying can be used to form polymer micro-nano particles with highly controllable size, dispersion, certain shape and unique surface morphology. The combination of the two can quickly realize the composition of micro/nano particles.

The preparation of nanoparticle composite by the combination of ultrasonic spraying and electrostatic spraying has many advantages, including the following points:
1) Excellent preparation effect of nanoparticles: ultrasonic spraying can produce very fine droplets, combined with electrostatic spraying, can achieve accurate control and uniform dispersion of nanoparticles.
2) Efficient use of raw materials: combined with ultrasonic spraying and electrostatic spraying technology, raw materials can be used more effectively and waste generation can be reduced. Due to the controllability of particle size, the utilization efficiency of raw materials can be better mastered.
3) Enhanced surface uniformity: Electrostatic spraying forms a uniform thin layer on the surface of the nanoparticle composite, which helps to improve the surface uniformity of the composite. This has important implications for some applications, such as coating materials or drug delivery materials.
4) The process conditions can be regulated: the combination of the two technologies can flexibly adjust the process conditions according to needs, including ultrasonic amplitude, electrostatic field strength, etc., to meet the requirements of different applications for nanoparticle composites.
5) Production efficiency: ultrasonic spraying and electrostatic spraying are relatively efficient preparation technologies, which can improve production efficiency when combined.
The nanoparticle composite technology of ultrasonic spraying and electrostatic spraying has the advantages of precision, controllability and high efficiency, so it has a broad application prospect in the field of nanomaterials preparation.
Ultrasonic atomization component: The standard is equipped with an ultrasonic atomizing nozzle, the generator is located inside the electrical box, and is controlled by the panel to achieve high flux atomization capability of low viscosity liquid. When used independently, nanoparticle deposits can be prepared.


Product link:https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/multifunctional-electrospinning-machine-e04-001.html
Electrospun nanofibers have wide application prospects in tissue engineering because of their high specific surface area, biocompatibility, degradability and versatility. This content selects 6 relevant literatures to help you quickly understand the application progress of electrospinning nanofibers in the field of tissue engineering.

Main content: The structure, function and application of 3D tissue engineering scaffolds vary depending on the selection of electrospinning materials and methods and the post-processing of electrospinning scaffolds. In this paper, the latest research progress of 3D nanofiber scaffolds for electrospinning and the preparation methods of various 3D electrospinning scaffolds are reviewed, and their advantages and disadvantages are compared. Finally, the challenges and prospects of 3D electrospinning scaffolders are discussed, which provides a new idea for their application in biomedicine field.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00170-7

Main content: This study presents an injectable, biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel, made from short electrospun poly-L-lactic acid nanofibers embedded in a collagen matrix, that can be injected into joints and self-generate local electrical signals under ultrasonic activation to drive cartilage healing. In vitro experimental data showed that the piezoelectric hydrogel under ultrasound could enhance cell migration, induce TGF-β1 secretion from stem cells, and promote chondrogenesis. In vivo, rabbits with osteochondral critical size defects receiving ultrasonic-activated piezoelectric hydrogels showed increased subchondral bone formation, improved hyaline cartilage structure, and good mechanical properties close to healthy natural cartilage. This piezoelectric hydrogel can be used not only for cartilage healing, but also for other tissue regeneration, which is of great significance in the field of regenerative tissue engineering.
Original link:
href="https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41594-y" https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41594-y

Main content: In this study, a high-elastic zein microfiber smart scaffold with a three-layer structure was designed for motion tracking in the unpacked state. By introducing a highly reactive epoxy resin, a tightly cross-linked protein network is effectively established and provides a wide range of stretsibility (360% stretch range) and ultra-high elasticity (99.91% recovery) to the fiber substrate in the wet state. A silver conductive sensing layer was constructed on the protein fibers with the help of a polydopamine bonding layer, resulting in a scaffold with wide strain sensing range (264%), high sensitivity (measurement factor up to 210.55), short response time (<70 ms), reliable cyclic stability, and long service life (up to 30 days). The unpackaged smart scaffold can not only support cell growth and accelerate wound healing, but also track skin and body movement, triggering an alarm once the wound is excessively deformed.
Original link:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c03087

Main content: This study first introduces the structure and various structures of electrospun fiber scaffolds, as well as various commonly used drug types. We then discuss some representative strategies for controlling drug delivery in electrospun fibers, with particular emphasis on the design of endogenous and exogenous stimulus-responsive drug delivery systems. Subsequently, the recent progress of call-spun fiber scaffolds in controlling drug delivery in tissue engineering (including soft tissue engineering (such as skin, nerve, and heart repair) and hard tissue engineering (such as bone, cartilage, and musculoskeletal systems) as well as in cancer treatment is summarized. In addition, the future direction and challenges of electrospun fibers for controlled drug delivery are also presented, aiming to provide insights and perspectives for the development of smart drug delivery platforms to improve the clinical efficacy of tissue regeneration and cancer therapy.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00198-9

Main content: One-dimensional activated carbon nanofibers were synthesized from polyacrylonitrile electrostatic spinning nanofibers by continuous processes such as stabilization, alkali treatment, calcination and grinding. Two different sets of electrostatic spun polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofiber pads containing ACNF NPs were prepared, namely, surface modified NPs deposit pad (ACNF@PCL) and NPs binding pad (ACNF-PCL), and their potential as scaffolders for skin tissue engineering was investigated. Acnf-pcl pads with lower concentrations of ACNF NPs have greater potential to support cell growth, thus ensuring their possible impact on skin tissue regeneration.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00608-x

Main content: This paper reviews the research progress of electrospun nanofiber/hydrogel composites in tissue engineering, summarizes several preparation methods, advantages and disadvantages of nanofiber/hydrogel composites, and introduces the application of these nanofiber/hydrogel composites in skin, blood vessel, nerve, bone and other tissue engineering in detail. Finally, the future research direction of nanofiber/hydrogel scaffold materials is proposed, which provides reference for the preparation of functional nanofiber/hydrogel composite materials in the field of tissue repair in the future.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023.04.015
Although electrospun nanofibers have a wide range of applications in the field of tissue engineering, there are still some challenges, such as:
1. Mechanical properties are not enough to withstand the physiological load of human tissue, need to further improve the mechanical properties of the material.
2. Some functional electrospun nanofiber scaffolds may lose their function after long-term use, and the durability and stability of the materials need to be solved.
3. Although the electrospinning nanofibers can be prepared by choosing biocompatible materials, more in-depth research on the biocompatibility of the materials is still needed to ensure its safety in vivo.
Solving these challenges will help promote the application and development of electrospun nanofibers in the field of tissue engineering.
Related link: https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/multifunctional-electrospinning-machine-e04-001.html
Electrospinning nanofiber films have attracted great interest due to their excellent waterproof and breathable properties, which stem from the presence of interconnected and hydrophobic channels in these reinforced textiles. These unique properties give them great potential in various fields, including the application of medical dressings, masks and protective clothing. However, they have also raised concerns about their durability, impaired water resistance, limited air permeability, inadequate mechanical strength, and high production costs. In addition, the manufacturing process of electrospinning waterproof breathable film (WBM) can have an adverse impact on the environment, hence the need for improved sustainability and ecological compatibility.

Based on this, Professor Ding Bin's team at Donghua University gave a comprehensive overview of the potential and challenges of electrospinning waterproof breathable membranes, as well as improvement strategies and future research directions. Related content under the title "Advancements in Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes for Improved Waterproofing and Breathability", Published in the journal 《Macromolecular Materials and Engineering》.
Key points of this article:
1. The preparation method, characterization technique and performance evaluation method of electrospinning nanofiber film are introduced in this paper.
2. The application of electrospinning nanofiber film in waterproof and breathable material is discussed.
3. In addition, the environmental impact and sustainability problems in the preparation of electrospinning nanofiber film are also discussed, and corresponding solutions are proposed.

These features include high porosity, customizable porous structure, and modifiable wetting characteristics. These internally interconnected and hydrophobic channels allow water vapor and air to diffuse from the interior to the external environment, while effectively repelling water molecules and preventing water from penetrating from external sources. The holes inside the membrane material are designed to be small enough to prevent the penetration of liquid water droplets, but large enough to facilitate the transport of water vapor. These properties make electrostatic spinning nanofiber membranes ideal for use in waterproof, breathable clothing, footwear, and other products.
1. Fine-tuning of parameters: Fine-tuning of the structural parameters of the membrane, such as pore size, porosity and thickness, is essential to achieve a balance between air permeability and waterproof performance. This can be achieved by optimizing the manufacturing process and controlling the formation and conditions of the membrane to achieve a uniform, dense and defect-free membrane structure.
2. Multi-component spinning: Multi-component spinning includes the use of two or more polymers to prepare a composite film with enhanced properties. This technology allows for a combination of different materials to achieve a balance between water resistance and air permeability.
3. Surface modification: Surface modification includes the use of chemical or physical treatment to change the surface characteristics of the film. This technology can improve the hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity of the film, thus improving the water resistance or air permeability of the film.
4. Nanoparticle incorporation: Nanoparticle incorporation of the film can improve its mechanical strength, durability and waterproof performance.
5. Porous membrane structure: porous membrane structure, honeycomb membrane structure, multi-layer composite membrane can enhance the waterproof and breathable performance.

Figure 2 a) wvtr comparison of PU/FPU films. b) WVTR of PU/FPU films with different porosity is expressed on a logarithmic scale. c) Hydrostatic pressure measurement. d) DMF-FPU/PU system phase diagram. e) Schematic diagram illustrating the co-occurrence of charge dissipation and non-solvent-induced phase separation during jet stretching and solidification. f) RET value and WVTR of different RHs. g) Molecular composition of synthetic C4FPU and schematic diagram of its application. h) Schematic diagram showing surface enrichment of the fluorinated part of the membrane. i) stress-strain curve and j) antibacterial activity of PU/C4FPU/AgNO3 membrane.

Figure 3 a) Configuration and visual description of the electrostatic spinning process of SBS electrostatic spinning fiber felt/polyester composite. b) The deformation diagram of SBS electrostatic spinning fiber pad under the action of stress, comparing the deformation of beaded and beaded fiber pad. c) Schematic diagram of double-needle electrospinning device. A diagram showing the behavior of water droplets on different nanofiber surfaces :d) the generation of nano roughness, e) the establishment of Cassie state, and the occurrence of Wenzel-Cassie mixed state PANWA-NFs. f) stress-strain curve

Figure 4 a) Schematic diagram of the production process of pan film modified with ASO/SiO2 NPs (PAN@ASO/SiO2). b) Measurement of WCA and advance contact Angle (adv) of PAN@ASO/SiO2 at different SiO2 NP concentrations. c) PAN@ASO/SiO2 changes in adv when exposed to a highly alkaline solution with pH 12. d) Steps for preparing WBA/ TiO2-modified PA-6(PA-6@WBA/TiO2) film. e) The UV protection factor value of the fiber film PA-6@WBA/TiO2 varies with the TiO2 nanoparticle concentration. f) Images of E. coli colonies treated with fibrous membranes under dark and visible light conditions. g) Morphological changes of PA-6@WBA/TiO2-3 membrane Escherichia coli cells before and after visible light irradiation.

Figure 5 a) Schematic diagram of the production process of polytetrafluoroethylene porous film. b) WCA of untreated PA-6 membrane and PA-6 membrane treated with PU solution. c) Schematic diagram of WCA changes of PA-6 membrane before and after treatment with PU solution.
1. Material selection: Choose environmentally friendly and sustainable materials to produce film, which can significantly reduce the impact on the environment. For example, using biodegradable polymers or natural materials.
2. Green processing technology: the implementation of green processing technology, such as the use of non-toxic solvents, reduce energy consumption, minimize waste generation, contribute to the sustainability of the manufacturing process.
3. Recycling and waste management: Developing recycling and proper waste management of materials used in manufacturing can reduce environmental footprint and promote ecological compatibility.
4. Environmental protection post-treatment: Use of environmental protection post-treatment technology to minimize the impact of electrospinning film preparation process on the environment.

Figure 6 a) Schematic diagram of PMHS/PU film production. b) Preparation process diagram of PU/HSG composite film. c) Silicone terminal alteration. d) Schematic diagram of preparation of PU/SiO2 film. e) WVTR and permeability of PU/SiO2 film. f) Schematic diagram of PU/SiO2 nanofiber film preparation. g) Integrated reaction of SiO2 particles with PU/4,4 '-MDI-0.4/APTES-2.

Figure 7. Challenges and future trends of electrospinning nanofiber WBMs.
Original text link: https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202300312
Related link:
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/multifunctional-electrospinning-machine-e04-001.html
Electrospinning nanofibers have excellent properties in battery electrodes and diaphragm materials because of their large specific surface area, high porosity and controllable thickness. Therefore, electrospinning nanofibers have a wide range of applications in batteries field.

However, nanofibers in electrode materials often use sulfur and transition metal compounds. If the nanofiber is prepared in an open environment, oxidation, hydrolysis and other reactions will occur, which will ultimately affect the electrochemical properties of the product, but also make the dose-effect relationship of the material difficult to be accurate, and the experimental data fluctuate greatly. Therefore, when preparing such materials, the water oxygen content of the spinning space is very strict.

1. The machine needs to effectively prevent the diffusion of H2O, O2, N2 molecules in the air and the diffusion of toxic molecules out of the glove box, low leakage rate. Water oxygen concentration should reach 0.01PPM.
2. Low water oxygen content, large gas adsorption, long regeneration interval.
3. Water oxygen detection is accurate.
The MBRT Nanofiberlabs electrospinning machine E04S can prepare nanofibers in the absence of water and oxygen.
Product link:
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/multifunctional-electrospinning-machine-e04-001.html

Traditional wound dressings cannot keep the wound moist, do not promote wound healing, and cause secondary injury to the wound when changing the dressing. As a result, its performance is often poor. Electrostatic spinning nanofibers used in wound dressings have good absorptive properties, breathability and comfort, which not only help to promote wound healing, but also prevent infection. This content combs 5 research papers on electrospinning nanofibers in wound dressings to help you better understand their application progress.

Main content: In this study, the fiber membrane with a unique "core/sheath" structure was prepared by coaxial electrospinning. The shell layer was composed of nano-copper peroxide (CuO2), polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) and polycaprolactone (PCL), and the core layer was composed of PCL. When exposed to the moist internal environment of the wound, PVP in the nuclear layer gradually decomposes and releases embedded nano-Cuo2. Therefore, under the induction of weakly acidic wound microenvironment such as diabetes and bacterial infection, H2O2 and Cu2+ ions are released through chemical kinetic reactions, and then Fenton-like reactions are triggered to produce ·OH for antibacterial, and copper ion release is followed by inhibition of inflammation and promotion of angiogenesis. At the same time, the dissolution of PVP forms a unique nanogroove surface pattern on the nanofibers, which provides the required cell guidance function for accelerating skin regeneration.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202305100

Main content: Inspired by the radial branching structure of the Nymphaeaceae plant, the researchers proposed a programmable strategy to construct radially assembly nanofiber patches with rapid deployment characteristics and strong anti-fracture bearing capacity, which could promote their application in joint trauma during limb movement. In addition, this patch will be endowed with "on-demand" anti-inflammatory drug delivery in the inflammatory microenvironment due to matrix metalloprotease MMP-9 triggering GelMA coating degradation, while stromal cell-derived factor (SDF1α) "center-peripheral" gradient changes can stimulate MSC recruitment to the lesion site. These properties make radially assembled nanofiber patches a promising material for wound healing and other regenerative medicine applications.
Original link:https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202109833

Main content: Multi-functional electrospun fiber membranes (EFMs) with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, hemostatic and wound exudate absorption properties were constructed by loading Taxifolin (TAX) onto cyclodextrin metal-organic frameworks (CD-MOFs) and then onto polycaprolactone (PCL) scaffolds via electrospinning. The resulting EFM has a hydrophilic surface, which facilitates wound adhesion and enhances hemostasis. By collecting wound exudate, the cascade release of TAX is triggered to reduce wound bacterial infection and reduce the expression of inflammatory factors. This also promotes collagen deposition, angiogenesis and contraction and migration of myofibroblasts, and promotes remodeling and repair of wound tissue.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.147262

Main content: We used electrospinning and fiber fracture composite technology to prepare drug-resistant bacterial chitosan/cellulose nanofiber/tannic acid (CS/CNF/TA) hydrogels with good wound treatment ability. The antibacterial performance of the hydrogel against drug-resistant bacteria was superior to 99.9 %. The hydrogel is rich in catechol groups, which can adhere to the surface of the tissue and avoid the hydrogel falling off during movement. In addition, it shows extraordinary hemostatic ability during the bleeding stage of the wound and regulates the wound microenvironment by absorbing water and moisturizing. In addition, CS/CNF/TA also promoted the regeneration of blood vessels and follicles and accelerated the healing of infected wound tissue, with a healing rate of over 95% over a 14-day period.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121687
Related link:
https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/product/multifunctional-electrospinning-machine-e04-001.html
Chemical fiber textiles often appear the phenomenon of floating silk, there are many reasons, mainly including the following aspects:
Many chemical fiber textiles will appear after a period of use, which is caused by the transparency of the fiber. When the fibers are transparent, the phenomenon of beading occurs. This situation usually appears in the use of a longer time of chemical fiber textiles.
High humidity is also one of the reasons for the phenomenon of floating silk in chemical fiber textiles. This is because the moisture in the air will be inhaled and stored by the textile, resulting in reduced friction between the fibers and the formation of electrostatic force between the fibers, resulting in the phenomenon of floating silk.
Chemical fiber textiles produce static electricity when rubbed, so they often float silk. This is due to the enhancement of electrostatic force between the fibers, mainly due to friction between the fibers.
In response to the above problems, we can take the following measures to reduce the phenomenon of chemical fiber spinning.
Because high humidity can lead to increased electrostatic force between fibers, indoor humidity can be reduced to reduce the phenomenon of silk drift. You can ventilate the room well or use equipment such as humidifiers and dehumidifiers.
In the manufacture of chemical fiber textiles, the choice of high-quality yarn is also very important. High quality yarn strength, strong durability, can reduce the occurrence of silk drift phenomenon.
The correct cleaning of chemical fiber textiles is also important, you can choose to use neutral detergent for cleaning, so as not to cause damage to the yarn.
Chemical fiber textiles usually have the phenomenon of floating silk, which is caused by a variety of reasons, such as fiber transparency, high humidity and static electricity. However, we can reduce the occurrence of filaments with suitable solutions, such as reducing indoor humidity, choosing high-quality yarn and proper cleaning.

Product link:https://www.nanofiberlabs.com/products-category/lab-scale.html
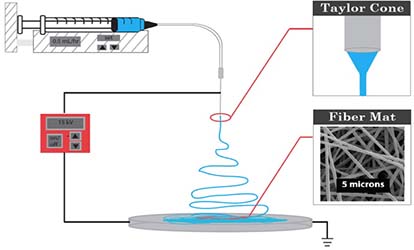
Figure Electrospinning principle diagram
Electrospinning technology is a one-dimensional nanofiber preparation technology. Its advantages are simple manufacturing device, low spinning cost, many types of spinnable polymers, and controllable spinning process. The basic principle is: in a high-voltage electrostatic field, when the electric field force of the charged polymer solution or melt droplet is greater than the surface tension, the polymer is drawn and refined under the action of the electric field, and this process is accompanied by solvent evaporates and the fibers solidify to form nanofibers, which are recently deposited on the receiving device. Electrospun nanofibers, as a kind of nanomaterials, have the characteristics of high specific surface area, large aspect ratio and high porosity. They are used in filtration separation (air filtration, water filtration, cell filtration, oil-water separation), biomedicine (tissue engineering, Drug release, wound repair), nanocatalysis (photocatalysis, electrode catalysis, enzyme catalysis, precious metal catalysis), sensors (vibration frequency sensor, resistance sensor, photoelectric sensor, optical sensor, ampere sensor), new energy (dye-sensitized solar energy) Battery photoanode materials and electrolyte materials, lithium ion battery diaphragm and electrode materials), nano luminescent materials (oxide semiconductor luminescent materials, sulfide semiconductor luminescent materials, rare earth element doped luminescent materials, organic luminescent materials), magnetic materials (ferrite Bulk nanofiber magnetic materials, metal nanofiber magnetic materials, inorganic/polymer composite nanofiber magnetic materials), composite reinforcement materials, food packaging materials, cosmetic materials (beauty masks), sound-absorbing materials, high-temperature thermal insulation materials (inorganic ceramic nanofibers) ), nano-carbon fiber and other fields, have broad application prospects.

Figure Nanoscience and technology
Nanoscience and technology is the study of the properties and interactions of substances (including atoms and molecules) on the nanometer (1nm=10-9m) scale (between 0.1nm and 100nm), as well as multidisciplinary high-tech technologies that utilize these properties. The ultimate goal is to directly manufacture products with specific functions based on the characteristics of atoms and molecules on the nanoscale and substances on the nanoscale, and achieve a leap in production methods. Nanoscience generally includes the research fields of nanoelectronics, nanomechanics, nanomaterials, nanobiology, and nanochemistry.

Figure Electrospun nanofiber SEM
The size of nanofibers is widely defined, and there is currently no standard definition. In a narrow sense, nanofibers refer to fibers with a diameter in the range of 1-100nm. Broadly speaking, fibers below 1um can be called nanofibers. In addition, from the perspectives of spinning technology, cost, and practicality, generally, fibers that contain nanostructures and are endowed with new physical properties can also be classified as nanofibers, such as fibers doped with functional nanoparticles (already Used in various functional fibers such as antibacterial, flame-retardant, anti-ultraviolet, far-infrared, antistatic, electromagnetic shielding, etc.). The size effect of nanofibers is very significant, showing many novel properties in light, heat, magnetism, electricity, etc., so it has received great attention from researchers and is expected to be used in clothing, food, medicine, energy, electronics, paper, aviation and other fields . Electrospun nanofibers are difficult to exist alone. They usually exist in the form of nanofiber aggregates and nanofiber membranes, which are similar to common plastic films, non-woven fabrics and other membrane materials. They are essentially plastic or inorganic (inorganic nanofibers membrane), there is no special toxicity in itself, so you can use it with confidence.
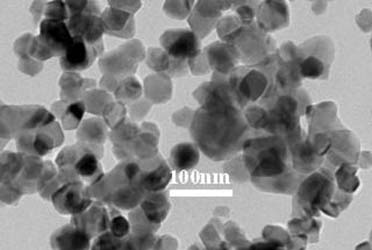
Figure ZnO Nanopowder
Nanomaterials can be roughly divided into four categories: nanopowder, nanofiber, nanomembrane, and nanobulk.
Nano-ceramics: Nano-ceramic materials developed by using nano-technology use nano-powders to modify existing ceramics. By adding or generating nano-scale particles, whiskers, wafer fibers, etc. into the ceramics, the crystal grains, grain boundaries, and their combination between them has reached the nanometer level, which greatly improves the strength, toughness and superplasticity of the material.
Nano powder: also known as ultrafine powder or ultrafine powder, generally refers to powder or particles with a particle size of less than 100 nanometers. It is a solid particle material in an intermediate state between atoms, molecules and macroscopic objects.
Nanofiber: refers to a linear material with a nanometer diameter and a large length. Electrospinning is a simple and feasible method for preparing nanofibers.
Nano film: Nano film is divided into particle film and dense film. The particle film is a thin film in which nanoparticles are stuck together with very small gaps in the middle. Dense film refers to a thin film with a dense film layer but with a nano-level crystal grain size.
Nano-bulk: Nano-bulk is a nano-crystalline material obtained by high-pressure molding of nano-powder or by controlling the crystallization of liquid metal. The main uses are: ultra-high-strength materials; smart metal materials, etc.
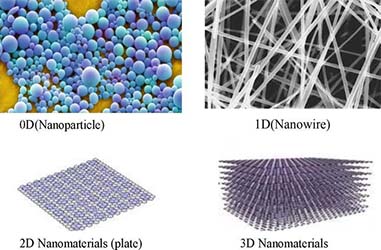
Figure Four types of nanomaterials
The broad definition of nanomaterials is: at least one dimension in the three-dimensional space is at the nanometer scale (nanophase materials) or structural materials composed of them as basic units (nanostructured materials). The basic units of nanomaterials can be divided into four categories: zero-dimensional, one-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional. Zero-dimensional means that the size of the material in the three dimensions of space is nano-scale, such as nanoparticles and atomic clusters; one-dimensional means that the size of the material in both dimensions of space is nano-scale, such as nanorods, nanotubes and nanofibers ; Two-dimensional means that the size of the material is nanoscale in only one dimension of space, such as nanosheets, ultra-thin films, multilayer films, and superlattices. Three-dimensional refers to the three-dimensional scale in space, such as nano-flowers and nano-balls.
It may be that the concentration of the spinning solution is too low, or the molecular weight of the polymer is too small.
Electrospinning, also called polymer injection and electrostatic stretching spinning process, is greatly different from traditional ways. Firstly, polymer solution or melt takes with thousands of high-voltage electricity. And electric polymer droplets are accelerated at the top of capillary Taylor cone under the influence of the electric field. Secondly, when the electric field power is strong enough, polymer droplets will inject a thin stream against surface tension, during which solution will evaporate or solidify. Finally the thin stream will be collected by collector, forming a non-woven cloth fibrofelt. During electrospinning process, droplets generally have electrostatic tension in an electric field, and therefore, when injection stream runs from capillary end to collector, it will accelerate, and induces injection stretching in the electric field.
Nanofiberlabs provides customized services for electrospinning equipment, such as customization of high-voltage power supply, electrospinning nozzle, type and speed of collection device, etc.
We are a manufacturer of electrospinning equipment with rich experience in manufacturing, as well as experience in nanomaterials manufacturing. Both experimental and industrial machines are available. Contact us by email or by submitting the customer form. Tell us your needs, we will provide customers with technical solutions.