Copyright © 2022 Foshan MBRT Nanofiberlabs Technology Co., Ltd All rights reserved.Site Map
Directory:
1. Introduction
2. Preparation method
3. Application field
1. Introduction:
Microsphere refers to a particle dispersion system formed by drug dispersion or adsorption in a polymer or polymer matrix. There are many carrier materials for preparing microspheres, mainly including natural polymer microspheres (such as starch microspheres, albumin microspheres, gelatin microspheres, chitosan, etc.) and synthetic polymer microspheres (such as polylactic acid microspheres). Microspheres are small spherical structures typically made of nanoscale materials. Their diameter is usually between a few micrometers to a few hundred micrometers, so the manufacturing technology known as microspheres has been widely used.
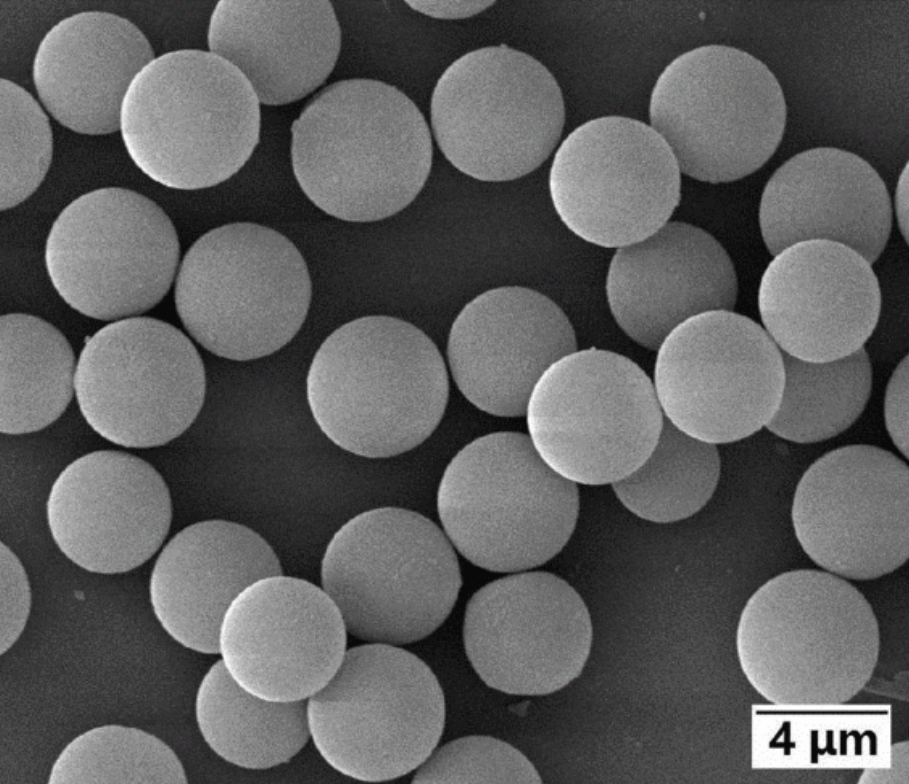

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of microspheres
2. Preparation method:
Microsphere preparation is a commonly used experimental technique for preparing small particles or microspheres with specific shapes and sizes. At present, there are emulsion volatilization, phase separation, spray drying, lotion polymerization, hot melt extrusion, microfluidic technology and other methods to prepare microspheres. Let the editor introduce these methods below.
2.1 Emulsion evaporation method:
The emulsified solvent evaporation method is most commonly used due to its simplicity and practicality. The emulsification evaporation method mainly includes O/W (oil in water) emulsification method, O1/O2 emulsification method, and double emulsion in liquid drying method. The O/W emulsification method is suitable for the preparation of lipid soluble drug microspheres, while the latter two methods are commonly used for the preparation of water-soluble drug microspheres.
(1) O/W emulsification method:
Add organic solvents containing drugs and polylactic acid to the aqueous phase containing emulsifiers, and form an O/W type emulsion through mechanical stirring or ultrasound. Remove the internal organic solvents, and polylactic acid and drug deposit to form microspheres.
(2) O1/O2 emulsification method:
Microspheres can be prepared by emulsifying the dissolved organic phase of drugs and polymers in an immiscible organic phase containing emulsifiers.
(3) Double emulsion in liquid drying method:
This method is an improvement on the traditional emulsion solvent evaporation method. The aqueous solution or suspension of the drug is added to an organic solvent dissolved in a polymer, stirred or sonicated to form colostrum (W/O type), and then transferred to an aqueous solution containing a stabilizer to homogenize into a complex emulsion (W/O/W type). The organic solvent is removed, solid-liquid separation is performed, and washing and drying is performed to obtain the colostrum. People have also invented various methods of double emulsion, such as W/O/O, W/O/O/O.
2.2 Phase separation method:
The phase separation method involves adding a phase separation agent to a mixed solution of drugs and polymers to reduce the solubility of the polymer, allowing it to encapsulate the drug and form drug loaded droplets, which are then transferred to another organic non solvent and solidified into microspheres.
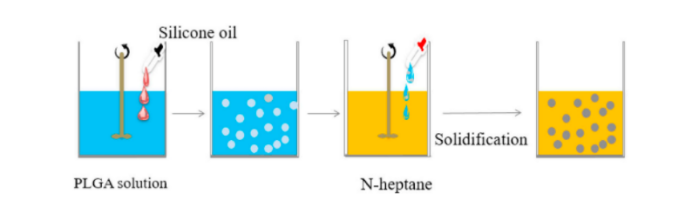
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of blank microsphere preparation
2.3 spray drying method:
The preparation of microspheres by spray drying is a method of spray liquid raw materials and excipients into hot drying media, so that the raw materials and excipients can be converted into dry powder in the spray dryer. The specific preparation process can be divided into three steps: the atomizer atomizes the raw material solution into small droplets → the dry gas solidifies and dries the small droplets → the dry particles are separated from the drying medium.
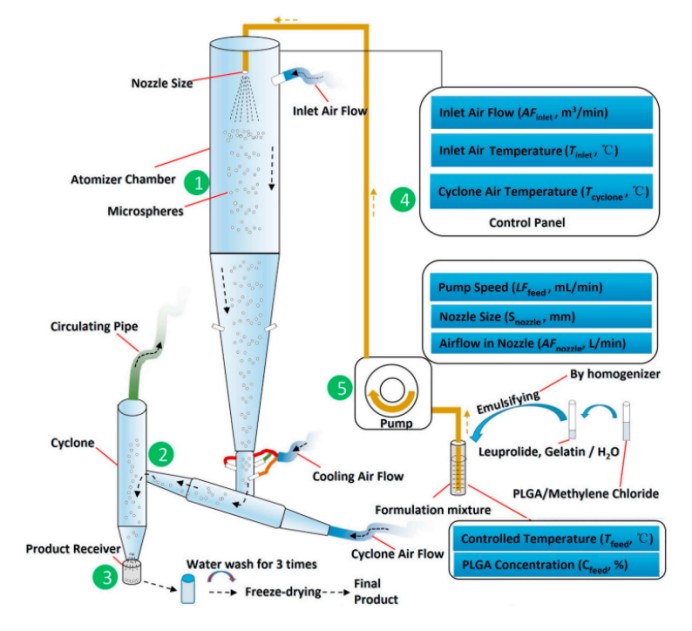
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of microspheres prepared by spray drying method
2.4 lotion polymerization:
Lotion polymerization is a polymerization in which monomer forms lotion in water with the help of emulsifier under mechanical agitation or vibration.
2.5 Hot melt extrusion method:
The hot melt extrusion method is to melt and mix drugs with polymers or other excipients to obtain uniformly distributed blocky products, which are then ground to obtain granular microspheres. The particle size and drug distribution of microspheres can be adjusted by controlling the melting temperature and grinding conditions.
2.6 Microfluidic technology:
Microfluidic technology is a new technology that can be applied to the preparation of microspheres. The basic principle is to make the two immiscible solutions meet in the microchannel, and under the action of external force or flowing shear force, they are divided into micron sized lotion droplets, and finally volatilize the solvent to solidify to obtain microspheres. Microfluidic technology is a preferred approach for the preparation of polymer microspheres.
The preparation of microspheres using microfluidic technology generally involves two steps:
(1) Emulsion droplet formation, refers to the emulsification of monomers or polymeric fluids in microfluidic channels to form droplets;
(2) The emulsion droplets are solidified or polymerized, and the emulsified droplets are then in-situ solidified (in microchannels) to form microspheres. The curing methods mainly include polymerization, freezing, and solvent evaporation.
So far, there are three commonly used emulsification devices for preparing microspheres or droplets using microfluidic technology: microfluidic devices containing stepped microchannels, T-shaped vertically staggered microchannels, and fluid focused microchannels.
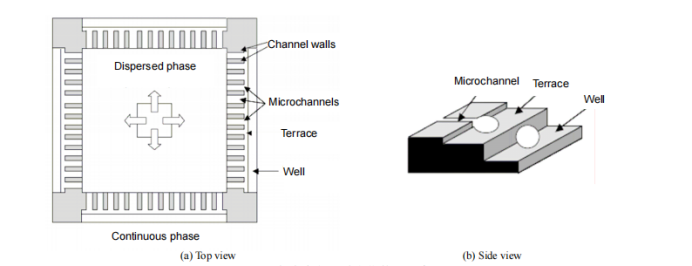
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of a stepped microchannel emulsification device
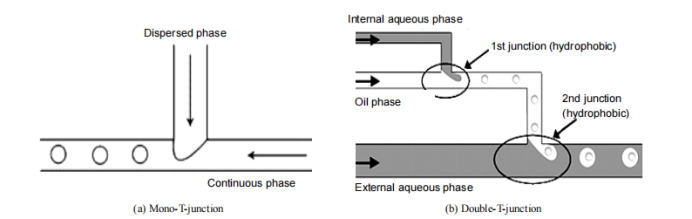
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of T-shaped vertical staggered microchannel emulsification device
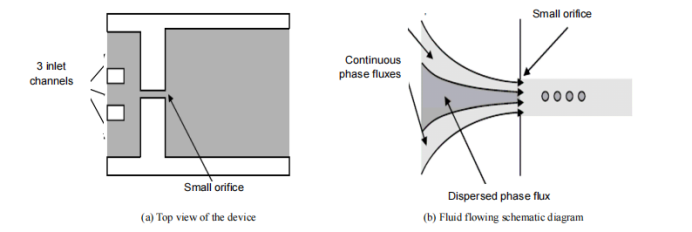
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of fluid focused microchannel emulsification
3. Application area:
The application of microspheres is extremely extensive and almost permeates all industries: whether it is medicine, food safety testing, medical diagnosis, water treatment, energy conservation and environmental protection, petrochemical, etc., advanced microsphere materials are indispensable.
3.1 In the field of medicine:
(1) After drug preparation into microspheres, the following objectives can be achieved: to mask the adverse odor and taste of drugs, such as fish liver oil, alkaloids, etc; Improve the stability of drugs, such as those that are easily oxidized β- Hu Luo Su, water sensitive aspirin, etc; Circulate liquid drugs for easy application and storage, such as oils, spices, and fat soluble vitamins; For sustained-release or controlled release drugs, inert matrix, film, biodegradable materials, hydrophilic gel, etc. can be used to make microspheres or microcapsules, which can make the drug controlled or sustained-release, and then be made into pull release or sustained-release preparations; Concentrate drugs in the target area.
(2) Microspheres are also used to manufacture drug delivery systems. These microspheres can be injected into the human body and then release drugs. Due to the precise control of the size and shape of the microspheres, the drug can be transported to the desired location, thereby improving the efficacy of the drug. In addition, microspheres can also be used for manufacturing artificial blood vessels and tissue engineering.
Figure 7 Medical field
3.2 In the field of food safety testing:
Due to its extremely high specific surface area and special surface groups, microspheres have selective adsorption function. Therefore, specially functionalized porous microspheres can capture extremely small amounts of harmful substances such as melamine in milk, pesticide residues in vegetables, and harmful substances in blood like a needle in a haystack, enabling us to accurately detect the content of these harmful substances. In addition, microspheres are also the heart of high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography columns, and high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography are currently one of the most important methods for detecting and analyzing harmful substances.

Figure 8 Food Safety Testing Field
3.3 In the field of water treatment:
Functional microspheres can remove organic impurities and metal ion components from water, and can be used to prepare ultrapure water in semiconductor, pharmaceutical, nuclear industries, and other industries. They can also be used to purify daily drinking water. Water washes the dirt for humans, but microspheres can eradicate the dirt in the water, achieving the goal of purifying water.
3.4 In the field of medical diagnosis:
Functional microspheres such as magnetic microspheres and multicolor fluorescent encoded microspheres can be widely used in immunoassay for high-throughput detection of multiple samples or targets. Due to the use of microspheres, we can conduct disease detection and diagnosis more quickly and conveniently.
3.5 In the field of chemical engineering:
Microspheres have been widely added to paints, coatings, papermaking, and plastics to improve the scratch resistance, wear resistance, and optical properties of products.
References:
[1]Wei Liming, Song Sankong, Song Xia, et al. New developments in microsphere preparation methods [J]. Chinese Pharmacologist, 2011 (11): 1682-1685. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2011.11.053
[2]Chen Zhi, Tian Jingzhen. Overview of the Application of Medicinal Microspheres [J]. Qilu Pharmaceutical, 2009, 28 (3): 164-167. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7738.2009.03.020
[3]Zhang Chengbin, Chen Yongping. A microfluidic microsphere preparation device: CN2011201198980.2 [P] [2023-08-22]
[4]Zhang Yan, Lei Jiandu, Lin Hai, et al. Research progress in the preparation of microspheres using microfluidic devices [J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2009 (5): 7. DOI: 10.3321/j. issn: 1009-606X.2009.05.033